Balloon Framing Example
A wood-frame construction method where wall studs run continuously from the sill plate to the roof plate, with floor joists nailed to the sides of studs using ribbon boards.
Examples:
1. Victorian-era homes (1850s-1930s) – Multi-story houses with ornate facades often used balloon framing for its ease of constructing tall, continuous walls
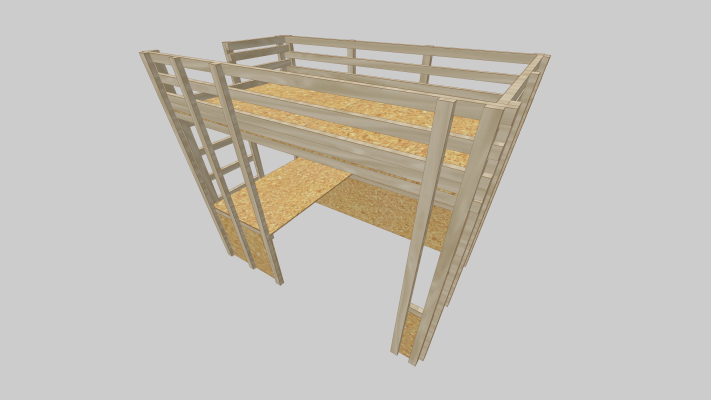
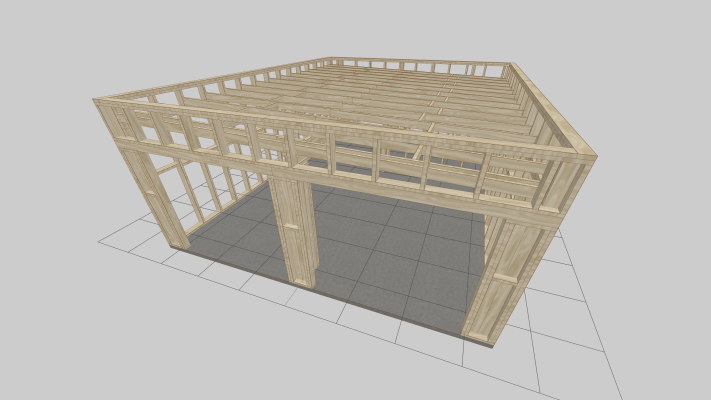
2. Two-story gable structures – As shown in the uploaded image, where studs extend uninterrupted through both floor levels to the roof peak
3. Narrow urban townhouses – Where tall, straight walls were needed on party walls between adjacent buildings
Materials Used:
- Dimensional lumber studs: typically 2×4 (38×89mm) or 2×6 (38×140mm), lengths 16-24 ft (4.9-7.3m)
- Ribbon board (ledger/firestop): 1×4 (19×89mm) or 1×6 (19×140mm) let into studs
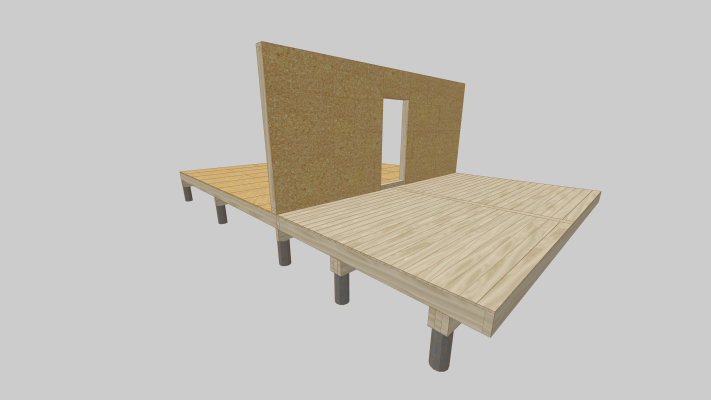
- Floor joists: 2×8 (38×184mm) to 2×12 (38×286mm)
- Sill plate and top plate lumber
Key Characteristics:
- Continuous studs span multiple stories
- Floor joists rest on ribbon boards notched into studs
- Requires fire blocking between floors (per IRC R302.11)
- Less common today due to fire safety concerns and long lumber requirements
Code References:
- IRC Section R602 (Wood Wall Framing)
- IRC R302.11 (Fireblocking)
- NFPA 5000 (Building Construction and Safety Code)
Show more




Sign in to leave a comment.